Many horse owners overlook warning signs that indicate serious health issues in their animals. Being vigilant about your horse’s behavior and physical condition is imperative for their well-being. Paying attention to subtle changes can lead to timely interventions, preventing potentially life-threatening situations. Whether it’s noticing changes in appetite, unusual behavior, or signs of discomfort, your ability to act quickly can make all the difference. Don’t let minor symptoms escalate into major problems; knowing these warning signs is key to maintaining a healthy and happy horse.
The Subtle Signs of Pain and Discomfort
Recognizing pain in your horse requires keen observation, as many signs can be quite subtle. Observe your horse’s posture, which may shift during standing or walking; a horse in discomfort may exhibit a tense stance, reluctance to move, or a decreased responsiveness during grooming. Changes in appetite, such as a refusal to eat or a sudden preference for softer feeds, can also indicate underlying issues. Close attention to your horse’s coat and overall demeanor will help you catch these signs early, allowing for prompt veterinary intervention.
Behavioral Changes: What Your Horse Isn’t Telling You
Behavioral shifts can provide critical insights into your horse’s discomfort. Watch for marked changes in attitude, such as increased aggression, nervousness, or even withdrawal from social interactions. A horse in pain may become less cooperative, avoiding work or resisting saddling. These behavioral changes can often be more pronounced than physical symptoms, making them vital for early detection of health issues that require immediate attention.
Physical Symptoms: When to Call the Vet
It’s crucial to act quickly when you notice physical symptoms that may indicate health problems in your horse. Things like persistent coughing, unusual sweating, or lameness should never be ignored. If your horse exhibits any signs of colic—like rolling, kicking at the belly, or lack of normal bowel movements—seek veterinary assistance without delay. Other symptoms such as a rapid heartbeat, high temperatures, or significant weight loss warrant immediate action as they can reflect serious health issues.
A horse’s physical symptoms will often guide you on when to consult a veterinarian. For instance, lameness can stem from a range of issues—from minor injuries to severe conditions like tendon tears. Equally alarming, a high fever (above 101.5°F) can indicate infection or systemic illness. Taking your horse’s vital signs regularly helps establish a baseline; variations might signal the need for immediate veterinary attention. Don’t hesitate to call a vet if you notice persistent symptoms or changes in demeanor, as early intervention can often mean the difference between a simple treatment and a more complex solution.

Nutrition Warning Lights: Eating Habits that Raise Red Flags
Observing your horse’s eating habits is imperative for detecting potential health issues. Sudden changes, such as decreased appetite or drastic shifts in food preferences, can indicate underlying problems that require your attention. Staying attentive to their dietary patterns will help you catch any alarming signs before they escalate into serious concerns.
Weight Fluctuations: The Silent Alarm of Dietary Issues
Significant weight changes in your horse often highlight dietary imbalances or health concerns. A horse gaining weight excessively may be consuming too many calories or lacking adequate exercise, while sudden weight loss can suggest metabolic disorders or gastrointestinal issues. Regular weight monitoring and a balanced diet are imperative to maintaining your horse’s health.
Unusual Eating Behavior: Signs of Dental or Digestive Problems
Any deviation from normal eating patterns should raise your alarm. If your horse exhibits signs such as chewing with difficulty, dropping food, or showing reluctance to eat, these behaviors may signal dental issues or digestive discomfort. A horse in distress may also start grazing tentatively or avoid certain types of feed, pointing to potential oral or gastrointestinal problems.
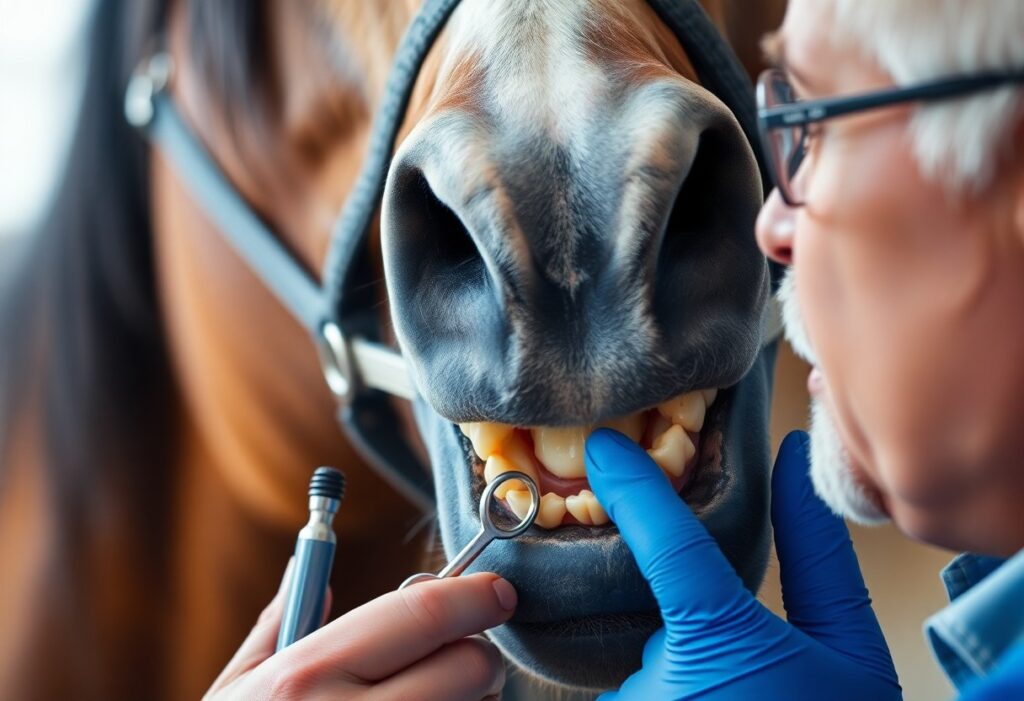
Unusual eating behavior can manifest in various ways, including excessive salivation, head tossing during meals, or even aggressive appetite changes. Such signs may indicate issues like sharp dental edges causing pain, or dental decay inhibiting their ability to chew properly. Likewise, if your horse refuses to consume roughage or shows colicky behavior post-feeding, consulting with a veterinarian is advisable to investigate possible digestive disturbances or other underlying conditions. Regular dental check-ups and observing any eating anomalies are vital in keeping your horse healthy.
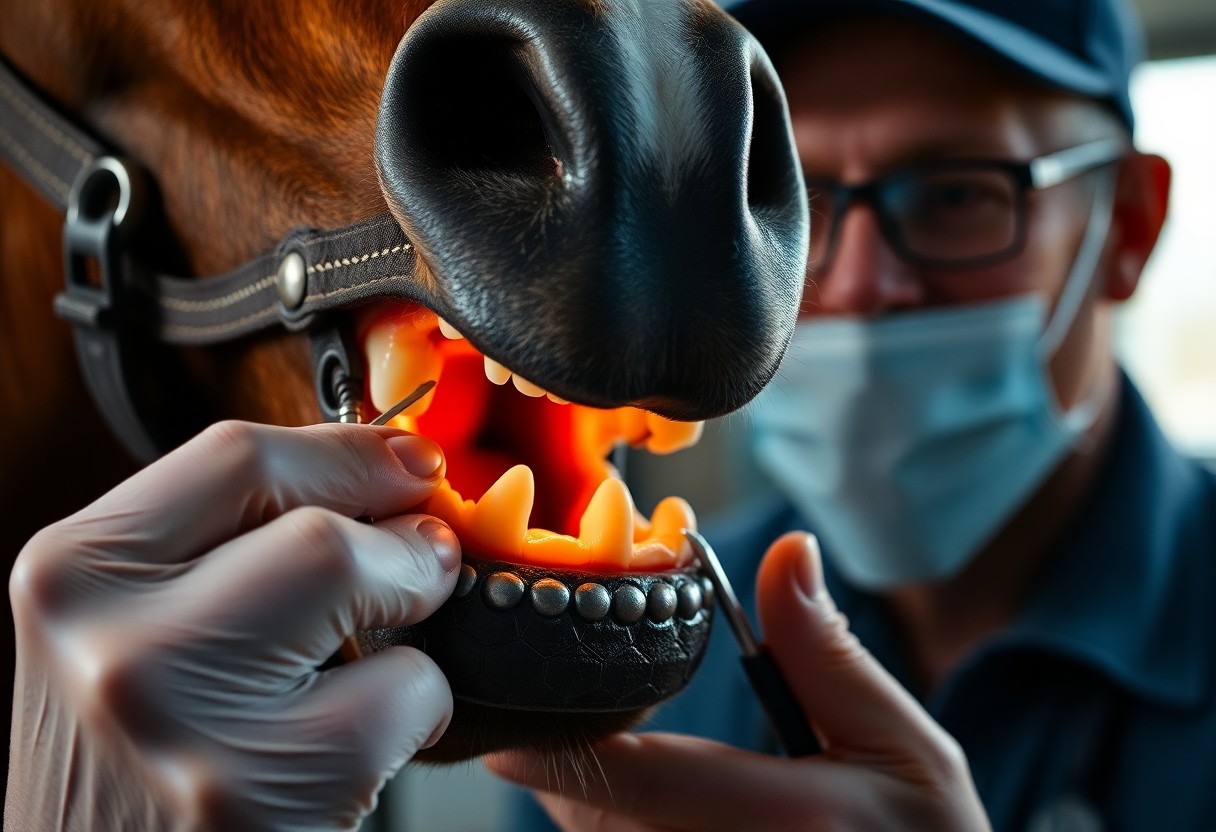
The Importance of Routine: Ignoring Regular Health Checks
Regular health checks are vital to maintaining your horse’s overall well-being. Skipping these appointments can lead to missed diagnoses of potential issues, such as dental problems, infections, or nutritional deficiencies. Routine examinations allow for early intervention and long-term prevention strategies that can save you from significant health complications and expenses in the future.
Vaccine and Deworming Schedule: Why Skipping Can Be Hazardous
Establishing a consistent vaccine and deworming schedule safeguards your horse against serious illnesses and parasites. Skipping vaccinations can leave your horse vulnerable to outbreaks of contagious diseases like West Nile Virus or Equine Influenza. Likewise, neglecting deworming can lead to worm infestations that compromise your horse’s health, resulting in weight loss, colic, or even death.
Hoof Care: The Foundation of Your Horse’s Health
Neglecting hoof care can lead to painful conditions such as laminitis, thrush, or abscesses. Regular hoof trims and checks are vital for your horse’s mobility and overall health, as hooves bear the animal’s entire weight and are susceptible to injury. Proper hoof care ensures optimal blood circulation and prevents chronic pain that can stem from shoeing problems or poor hoof growth.
Establishing a routine for hoof care directly impacts your horse’s comfort and performance. Each hoof should be trimmed every 6-8 weeks, depending on growth rates. Pay attention to any signs of lameness or changes in behavior that may indicate hoof issues. Regularly inspecting hooves for cracks, chips, and foreign objects can prevent complications. Consulting with a qualified farrier will ensure your horse has a proper fit and appropriate shoeing to enhance their mobility and prevent injuries.
Emotional and Psychological Health: Overlooked Indicators of Stress
Stress in horses often goes unnoticed, manifesting in subtle changes in behavior rather than overt signs of distress. You should pay attention to your horse’s body language, as signs like tail swishing, tight lips, and flattened ears can indicate discomfort or anxiety. Regularly assessing their emotional state is important in ensuring their overall health and well-being. Ignoring these signs can lead to deeper psychological issues that impact their performance and quality of life.
Changes in Social Behavior: Understanding Herd Dynamics
Your horse’s social behavior can provide valuable insights into their emotional health. If you notice your horse isolating themselves from the herd or displaying aggressive behavior towards peers, it may signal underlying stress or discomfort. Social interactions are crucial for horses; thus, significant changes can indicate that something is amiss in their environment or health.
Signs of Anxiety: Gauging Emotional Well-Being
Anxious horses often display a range of behaviors that may be easily overlooked, such as excessive pacing, repeated head tossing, or even cribbing. These signs of anxiety are often responses to stress triggers in their environment. Keeping a close eye on fluctuations in these behaviors can help you gauge emotional well-being and reveal if your horse needs specific interventions.
Mild anxiety in horses may be exhibited through fidgeting while tied or difficulty concentrating during training. More severe anxiety could manifest as persistent vocalizations, aggression, or severe withdrawal from social interactions, indicating that disorders may be developing. Case studies show that horses experiencing high levels of stress can suffer physical consequences, including digestive issues or compromised immune responses. Monitoring your horse’s behavior and addressing signs of anxiety promptly can prevent escalation and foster a healthier emotional state.

Assessing Lameness: Types and Causes to Monitor
Assessing your horse’s lameness requires careful observation of their movement and understanding the *causes* behind it. Common types of lameness include *forelimb* and *hindlimb* issues, often resulting from injuries or underlying conditions such as arthritis or tendonitis. It’s crucial to identify the specific type and monitor changes in behavior, as *lameness* can signify serious health concerns. Take note of their gait, any signs of discomfort, and location of the pain. Recognizing these factors early can lead to timely intervention.
| Type of Lameness | Common Causes |
| Forelimb Lameness | Injuries, Founder, Arthritis |
| Hindlimb Lameness | Tendonitis, Sprains, Bone issues |
| Intermittent Lameness | Soft tissue injuries, Infections |
| Chronic Lameness | Navicular syndrome, Osteoarthritis |
Recognizing Variations in Gait: What to Observe
Variations in your horse’s gait may indicate underlying issues that require attention. Pay close attention to deviations such as unequal strides, delays in response during transitions, or stiffness in the joints. Odd behaviors like reluctance to pick up pace or perform certain movements can also signal discomfort or pain. Monitoring *changes* in *gait* helps you address problems promptly and maintain your horse’s overall *health*.
Environmental Factors: How Changes Impact Equine Mobility
Various environmental factors can have a significant impact on your horse’s mobility. Changes like *temperature*, *humidity*, and *ground conditions* can influence their comfort levels and performance. For example, wet, muddy terrain might lead to slips or falls, whereas dry, hard ground can cause joint stress. Regularly assessing how your horse reacts to these *conditions* helps you maintain their well-being. After assessing the environment, note any behavioral changes that might indicate discomfort.
- Monitor *weather* changes
- Assess *ground surface* stability
- Evaluate *trotting* surfaces
- Consider *temperature* effects
- Analyze your horse’s *behavior* during different conditions
Environmental shifts such as heavy rainfall, heat waves, or sudden changes in terrain can greatly influence your horse’s mobility and comfort. For instance, icy surfaces can increase the risk of slips and falls, while extreme temperatures may cause fatigue or behavioral changes. Keeping a close watch on these factors ensures you’re prepared to adjust your horse’s routine accordingly. After monitoring environmental effects, be proactive in altering your horse’s activities to minimize risks.
- Insulate against *humidity*
- Provide a *consistent surface*
- Adjust *feeding* schedules
- Limit *exercise* during extreme weather
- Evaluate *comfort* based on environment
Summing up
Upon reflecting, it is vital for you as a horse owner to stay vigilant for warning signs that indicate potential health issues in your horse. By recognizing changes in behavior, appetite, or physical condition, you can take timely action to address any underlying problems. Ignoring these signals can lead to serious consequences for your horse’s wellbeing. Stay informed, be observant, and ensure your horse receives the care it needs to thrive.
FAQ
Q: What are the common signs of colic in horses?
A: Common signs of colic include pacing, rolling, looking at the abdomen, loss of appetite, and excessive sweating. If observed, consult a veterinarian immediately, as colic can lead to serious complications.
Q: How can I tell if my horse has a respiratory issue?
A: Symptoms of respiratory issues in horses include coughing, nasal discharge, labored breathing, and increased respiratory rate. If any of these signs are present, seek veterinary assistance to evaluate potential conditions.
Q: What should I do if my horse displays signs of lameness?
A: Signs of lameness include limping, reluctance to move, and changes in gait. It is imperative to assess the horse’s movement and consult a veterinarian for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.